Corporate Governance
Basic Policy
In addition to making contributions to social development, protection of life and environmental preservation, ISK strives constantly to respect our shareholders, customers, suppliers, local communities and employees while maintaining transparency in business activities abiding by laws and regulations.
In order to enhance corporate value by maintaining steady business growth and securing profitability, efforts to improve business transparency, reliability and corporate health are among management’s most important concerns, and we have worked hard to strengthen Corporate Governance through business management and enhanced internal controls founded on compliance.
Corporate Governance Structure
Structurally, we operate as a company with an Audit & Supervisory Board. In addition, we set Executive Management Committee under the Board of Directors in order to speed up decision-making by the Board of Directors and efficiently monitor and assess progress in important activities and projects. We have also introduced Executive Officer system with the aim of speeding up decision-making related to business activities.
Furthermore, we have the committees listed on the following page in order to strengthen our Corporate Governance.
The supervision and solving of important issues related to climate change, digital transformation (DX), and human capital are carried out on a company-wide basis by the Sustainability Promotion Committee, which is chaired by the Executive Director and President.
Corporate Governance Structure
*You can see the entire image in the figure by scrolling horizontally.
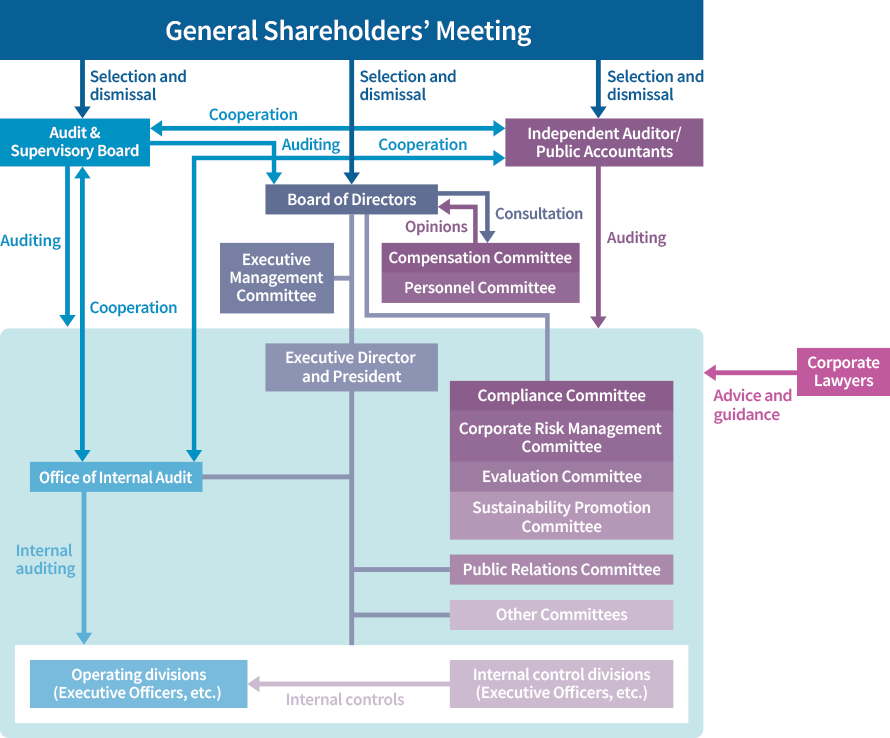
Major Organizational Entities Related to Corporate Governance
*You can see the entire image in the figure by scrolling horizontally.
| Board of Directors | Functions | The Board of Directors meets at least once a month to make decisions concerning important matters, report on the progress of operational execution and action plan implementation, review performance, and discuss and make decisions about how to deal with related issues. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Chairperson | Executive Director and President | |
| Members | Directors | ||
| Executive Management Committee |
Functions | The Executive Management Committee under the Board of Directors in order to speed up decision-making by the Board of Directors and efficiently monitor and assess progress in important activities and projects. | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Executive Director and President | |
| Members | The chairperson may require the attendance of such personnel as deemed necessary. | ||
| Audit & Supervisory Board | Functions | Audits the Board of Directors’ execution of its responsibilities, for example by attending Board of Directors and other important bodies and visiting departments regularly to exchange views in accordance with an audit plan adopted by the Audit & Supervisory Board, at least half of whose membership consists of independent outside Audit & Supervisory Board members. | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Inside Audit & Supervisory Board member | |
| Members | Inside Audit & Supervisory Board members, independent outside Audit & Supervisory Board members | ||
| Compliance Committee | Functions | Develops compliance structures based on the corporate philosophy and promotes corporate management predicated on compliance, for example by conducting compliance education and responding to the issues that come from its whistleblowing system | |
| Composition | Chairperson (CCO) | Executive Director and President | |
| Members | Directors, Audit & Supervisory Board Members, Headquarters Directors, Outside lawyer, ISK Labor Union chairperson, Directors of major subsidiaries | ||
| Corporate Risk Management Committee | Functions | Assesses and manages corporate risk incurred in the course of operations, formulates countermeasures, and deals with risks that have manifested themselves | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Executive Director and President | |
| Members | Inside Directors, Headquarters Directors | ||
| Evaluation Committee | Functions | Analyzes and evaluates the overall effectiveness of the Board of Directors | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board member | |
| Members | Independent Outside Directors, Inside Audit & Supervisory Board members, Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board members | ||
| Note: Five of seven positions on the committee (71%) are filled by independent Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board members. | |||
| Compensation Committee | Functions | As an advisory body to the Board of Directors, offers views in response to requests for advice from the President, who is delegated by the Board of Directors concerning the remuneration of Directors, Executive Officers and others. | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Independent Outside Director | |
| Members | Independent Outside Directors, Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board members | ||
| Note: All five positions on the committee (100%) are filled by independent officers. | |||
| Personnel Committee | Functions | Responds to inquiries from the President, who is delegated by the Board of Directors about the appointment of CEO’s successor and candidates for new Director or Audit & Supervisory Board member positions, as advising the Board of Directors | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Independent Outside Director | |
| Members | Independent Outside Directors, Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board members | ||
| Note: All five positions on the committee (100%) are filled by independent Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board members. | |||
| Public Relations Committee | Functions | Ensures transparency by disclosing information to investors in a timely manner, ensures the timely disclosure of information from Yokkaichi Plant to the local community, and promotes communication between our stakeholders and the company | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Executive Director and President | |
| Members | Directors, Representatives of Branches, Headquarters Directors, and others | ||
| Sustainability Promotion Committee | Functions | Controls actions for climate change, human rights, diversity and inclusion, health and productivity management, and DX. | |
| Composition | Chairperson | Executive Director and President | |
| Members | Inside Directors, Headquarters Directors, and others | ||
Independence Criteria for Outside Directors
Outside Directors and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board members are considered independent if none of the following applies to them.
-
1.A current or past (within the past 10 years) business executor*1 for ISK or its subsidiaries (collectively, “ISK Group”)
-
2.A current or past (within the past 5 years) principal ISK shareholder (i.e., a shareholder that owns 10% or more of ISK’s voting shares) or a business executor of the principal ISK shareholder
-
3.An ISK Group client, or a business executor of an ISK Group client, whose business dealings with ISK Group have accounted for more than 2% of ISK Group’s annual consolidated net sales for any of the most recent three fiscal years
-
4.An ISK Group supplier, or a business executor of an ISK Group supplier, whose business dealings with ISK Group have accounted for more than 2% of said party’s annual consolidated net sales for any of the most recent three fiscal years
-
5.An accounting professional, legal professional, or other type of consultant or a member of a consulting organization, which receives significant financial or other economic benefit*2 from ISK Group, other than Director remuneration
-
6.A party, or a business executor of a party, which receives or has received (within the past three years) significant financial contribution or assistance*3 from ISK Group
-
7.A spouse, relative within the second degree of kinship, or relative living together, of anyone that meets the criteria of #1 to #6 above
-
*1A person who meets the criteria stipulated in Article 2, paragraph (3), item (6) of the Ordinance for Enforcement of the Companies Act.
-
*2Normal remuneration averaging more than 10 million yen over the past three years.
-
*3Annual contribution or assistance totaling more than 10 million yen over the past three years.
Board of Directors
The Board of Directors meets at least once a month to make decisions concerning important matters, report on the progress of business execution, review performance, and discuss and decide on how to deal with related issues. Outside Directors supervise the business execution of ISK from an independent and fair standpoint without being directly involved in business execution.
The Executive Management Committee has been established under the Board of Directors to speed up decision-making at the Board of Directors and efficiently monitor and assess the progress of important business projects. It deliberates on overall important management matters and important business execution matters, and submits or reports to the Board of Directors as needed.
Auditing Structure
Corporate Auditors
Corporate Auditors attend important company meetings, including every meeting of the Board of Directors and the Executive Management Committee, constantly obtain information on the Company's operations from Directors, Executive Officers, employees and others in order to gain a full grasp of the Company's decision-making processes and business activities, and, as needed, conduct investigations, etc. of the status of the Company's business and assets.
Internal Auditing
The Office of Internal Audit (comprised of Director of such office and 10 other members), placed under direct control of the Executive Director and President, audits the status of compliance with laws and regulations, operation efficiencies and others pursuant to the Company's Internal Audit Regulations and annual audit plans. It is also responsible for the assessment and audit of internal control over financial reporting.
Basic Policy for the Internal Control System
-
The Company's "Basic Policy for the Internal Control System" has been set up in accordance with the provisions of the Corporation Law of Japan and the associated Enforcement Regulations of the Corporation Law. ISK's basic policy for internal control is outlined below;
-
1. Organizational Structures to Ensure that Directors and Employees Carry Out Work Activities Appropriately and In Line with Relevant Regulations and Articles of Incorporation
-
(1)The Company has adopted a management structure that places priority on compliance with laws, rules and societal norms.
-
(2)The Company has established a code of conduct that stresses the importance of compliance activities, and makes sure that Directors and employees follow them strictly.
-
(3)The Company has established a Compliance Committee, headed by the Director in charge of Compliance. This committee creates and implements plans to develop and maintain the compliance structure.
-
(4)Company policy dictates that should it be discovered that any Director or Employee of the Company has acted illegally, transgressed the Company's articles of incorporation, or acted in a way that raises the risk of a legal transgression, the incident must be reported immediately. Furthermore, all records of the reports and investigation are to be kept strictly confidential to ensure that those who report such incidents are not subject to repercussions.
-
(5)The Company has established an Office of Internal Audit to conduct regular audits, and which reports directly to the Executive Director President.
-
-
2. Recording and Managing Information Regarding the Activities of Directors
The Company maintains written records of the minutes of Board of Directors meetings, proposals submitted for consideration, and other important documents used in the course of Directors' duties. These documents are stored and managed in a way that corresponds to the legal regulations governing official documents, as well as all internal rules and regulations.
-
3. Rules and Structures Intended to Manage Risk
-
(1)A set of risk management guidelines has been established to express the Company's basic stance on risk management and to help guard against the risk of unexpected losses.
-
(2)The Company seeks to identify the various types of risk that emerge in the course of normal business activities, taking steps to ensure that each sector of business operations is aware of risk factors that may affect them, and takes steps to manage such risks.
-
(3)When events occur that could have an important impact on the Company's management and business activities, the Corporate Risk Management Committee takes action under the rules developed to manage risk, and assumes control of the Operating Divisions in order to minimize and address problems.
-
-
4. Structures to Ensure that the Execution Activities of Directors are Carried Out Efficiently
-
(1)The Board of Directors meets regularly, a minimum of once a month, to make decisions on important issues that effect the Company, and to oversee the activities of its Directors. In the case of priority issues that relate to business implementation, the Executive Management Committee, made up of Board members who are associated with the issue, discusses it first, and then reports to the entire Board for a final decision.
-
(2)The Company establishes clear and specific numerical targets for achievement, in an effort to improve management efficiency.
-
(3)The Board of Directors allocates work responsibilities to individual executives, and each Director's progress in completing the business tasks allocated to them is reported back to the Board of Directors.
-
-
5. Measures to Ensure that Business Activities Conducted by a Group Company, which Consists of the Company in Question and its Parent and Subsidiary Companies, are Appropriate
-
(1)The Company has established regulations and guidelines for the basic policies concerning execution of its affiliate companies' business activities, and for the various work processes concerning management of affiliated companies.
-
(2)Subsidiaries have the responsibility to uphold the same code of conduct as the Company, and must adhere to the same standards of compliance employed by the group as a whole.
-
-
6. Regulations Governing Employees Assigned to Assist the Duties of Corporate Auditors
Corporate Auditors may occasionally request that the Company assign personnel to assist them in carrying out their auditing activities. When this need arises, Directors cooperate with Corporate Auditors to select individuals who are able to provide effective assistance.
-
7. Measures to Ensure the Independence of the Aforementioned “Assistants” from the Influence of Directors
When Corporate Auditors ask to have employees assigned to assist with their activities, the views of the Board of Auditors are given top priority in selecting, transferring and evaluating such employees. This is intended as a way to ensure that the employees can act independently, without influence from Directors.
-
8. Structure for Reporting Information to Corporate Auditors, Including Reports Provided by Directors and Employees
-
(1)Corporate Auditors attend all meetings of the Board of Directors and the Executive Management Committee,as well as other important company meetings. They are also provided with access to information regarding all important proposals and resolutions made by management personnel.
-
(2)Directors and employees are required to provide necessary reports and information to Corporate Auditors and the Board of Auditors ,as stipulated in the Company's internal reporting regulations.
-
-
9. Structures to Ensure the Efficiency of Auditing Activities
-
(1)The Executive Director President holds regular meetings with auditors in order to exchange opinions regarding the condition of auditing activities and how to improve them.
-
(2)To ensure the effectiveness of auditing activities, Directors are responsible for ensuring that there is close cooperation between Corporate Auditors and the Office of Internal Audit.
-
-
10. Structures to Ensure the Reliability of Financial Reporting Activities
In order to ensure the reliability of financial reporting, the Company and its affiliate companies have established a structure to operate appropriately, and to improve and evaluate internal controls governing preparation of financial reports in accordance with the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law and other relevant regulations.
-
11. Basic Stance on Measures to Prevent Interaction with “Antisocial Groups”
-
(1)The Company strictly prohibits any activity or interaction with “antisocial groups” which may threaten public order or present a danger to the general public. The Company shall be resolute in avoiding any such contact, and will under no circumstances give in to unreasonable demands or pressure from any such group.
-
(2)In order to ensure that no such relationships or activities arise, a section of the General Affairs Division has been assigned specifically to cooperate with police, corporate lawyers and other outside organizations to combat the influence of corporate racketeers. This division will collect relevant information on a daily basis and establish a system to deal with unexpected incidents involving such groups.
-
-
Remuneration of Directors
-
Compensation for the Directors of the Company shall be determined with consideration for the factors listed below, taking into account the content of each Director’s duties and the Company’s condition.
Specifically:-
a)Compensation shall be fair and highly reasonable, enabling Directors to fulfill their accountability to stakeholders;
-
b)Compensation shall be structured to raise the incentive for Directors to increase corporate value;
-
c)Compensation shall be structured to enable the Company to secure and retain outstanding human resources as Directors;
Compensation shall be composed of “basic compensation,” “annual performance-linked compensation” and “long-term performance-linked compensation.” Compensation for Outside Directors shall be composed only of basic compensation due to their independence from business execution.
-
-
Basic compensation is paid as fixed monetary compensation based on the Officers Compensation Regulations, in amounts corresponding to the roles and responsibilities of each Director. Basic compensation is paid per calendar month, with a monthly amount paid on the same day as employees’ salaries.
-
Annual performance-linked compensation, paid as monetary compensation, is aimed at ensuring that compensation is linked to corporate performance and securing its objectivity. Whether annual performance-linked compensation is paid, and the amount of such payment, is calculated upon comprehensive consideration of the Company’s performance, including operating income and net income attributable to owners of parent, which represent the ultimate results of corporate activities, and corporate ESG performance, as well as individual performance evaluation. After the results for each fiscal year are finalized, they are discussed by the Compensation Committee, and the amount to be paid is decided at the first meeting of the Board of Directors held after the General Meeting of Shareholders. Annual performance-linked compensation is paid on the same day as employees’ summer bonuses.
-
Long-term performance-linked compensation is paid through a share delivery trust, composed of restricted stock units and performance share units. The restricted stock units are aimed at promoting the enhancement of corporate value by encouraging each Director to continuously hold the Company’s stock while in office, thereby participating in shareholder value. The number of shares to be delivered is calculated for each rank. The performance share units are aimed at promoting the enhancement of corporate value. The number of shares to be delivered is calculated with regard to ROE, which represents the ultimate results of corporate activities, and corporate ESG performance. Long-term performance-linked compensation is paid at a certain time based on the share delivery guidelines established by the resolution of the Board of Directors.
-
The proportions of basic compensation, annual performance-linked compensation, and long-term performance-linked compensation are proposed, taking into account each year’s financial results, etc., by an Executive Director, who is delegated authority by resolution of the Board of Directors. It is then referred to the Compensation Committee for deliberation, and determined by the Board of Directors, after discussion among the Executive Directors, based on the report by the Compensation Committee.
If the standard amounts of annual performance-linked compensation and long-term performance-linked compensation are paid, then the relative proportions of each type of compensation will be roughly as shown below.- Executive Director, President
Basic compensation (60%), annual performance-linked compensation (20%),
long-term performance-linked compensation (20%) - Other Directors
Basic compensation (65%), annual performance-linked compensation (20%),
long-term performance-linked compensation (15%)
- Executive Director, President
-
The details of compensation for individual Directors will be determined after deliberation by the Compensation Committee, which is composed of independent Outside Directors and independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members. The Compensation Committee will provide advice and recommendations, based on the information from officers’ compensation surveys carried out by thirdparty firms, and each member’s insight, before the decision is made. Compensation, etc. for individual Directors of the Company will be decided by the Executive Director, President, who is delegated authority by resolution of the Board of Directors. The Executive Director, President will evaluate the individual performance of each Director and determine compensation within the range approved by the Board of Directors, after deliberations by the Compensation Committee.
Policy on Cross-Shareholdings
ISK maintains an amount of cross-shareholdings deemed to build a smooth, stable, and ongoing relationship with business partners, in line with our business strategy. The status of cross-shareholdings is disclosed in our securities report. Other shareholdings have been appropriately reduced.
-
The reasonableness of currently held cross-shareholdings is regularly verified by the Board of Directors about some factors such as the adequacy of the purpose, the benefits and risks in the context of capital cost, of holding those shares. Based on the results of verification, the Board of Directors decides whether to continue holding or sell cross-shareholdings.
-
With regard to the exercise of voting rights arising from cross-shareholdings, our decision is made based on our comprehensive assessment, which includes the content of the proposal, the performance of the company, its management policies, and from the viewpoint of whether or not the resolution will increase shareholder value for the company, and even increase ISK’s corporate value.
