Functional Materials
Acicular Titanium Dioxide, FTL series
ISK has developed rutile-type acicular titanium dioxide by its own proprietary technology.
Utilizing its unique shape and hardness, the acicular titanium dioxide has been applied for reinforcing materials in plastics.
Due to physical strength of titanium dioxide, it can be hardly broken under strong mixing with resins.Due to its small size and high aspect ratio, it is expected to be applied for small and thin devices to reinforce them.
Owing to neutral pH and extremely low impurities, it can be applied for various resins.
Strengths
-
Strength 1Due to the inherent strength of titanium dioxide, acicular titanium dioxide is robust against strong shear forces occurring during plastic kneading and maintains reinforcing effects and other favorable properties.
-
Strength 2Despite its short major axis, its high aspect ratio makes it effective in small parts, thin-walled parts, and the like and renders a highly smooth surface.
-
Strength 3Since it is neutral and contains almost no impurities, it can be used in resin systems that are incompatible with alkalis.
Typical Applications
- Reinforcement of plastics, ceramics, metals, etc.
- Paint
- Paper
- Rubber
- Catalysts
- Friction materials
- Filter materials
Characteristics of Acicular Titanium Dioxide FTL Series
Due to the inherent strength of titanium dioxide, acicular titanium dioxide is robust against strong shear forces occurring during plastic kneading and maintains reinforcing effects and other favorable properties.
Despite its short major axis, its high aspect ratio makes it effective in small parts, thin-walled parts, and the like and renders a highly smooth surface.
Since it is neutral and contains almost no impurities, it can be used in resin systems that are incompatible with alkalis.
Photo 1 Electron micrographs of FTL series
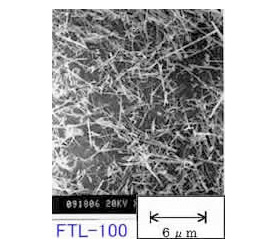


Table 1 Grade list
| FTL-100 | FTL-110 | FTL-200 | FTL-300 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White, Acicular crystal | |||
| Length1)(µm) | 1.68 | 2.86 | 5.15 | |
| Diameter1)(µm) | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.27 | |
| Composition (Crystal form) | TiO2 (rutile) | |||
| Specific Gravity | 4.2 | |||
| Specific Surface Area2)(m2/g) | 10~15 | 10~20 | 7~10 | 5~7 |
| Oil Absorption (g/100g) | 35~60 | 30~50 | 35~60 | 35~60 |
| pH | 6~8 | 6.5~8 | 6~8 | 6~8 |
-
1)volume-surface mean diameter measured with an image analyzer
-
2)conventional BET method
Fig.1 Reinforcing effect of acicular titanium dioxide (in PA resin)
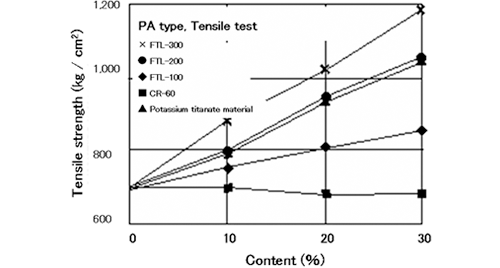
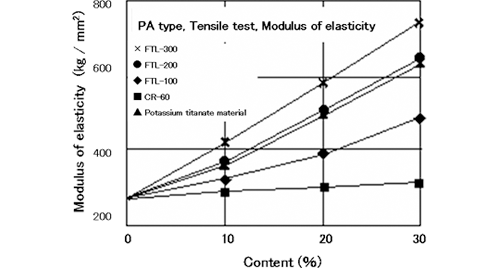
Table 2 Physical strength of acicular titanium dioxide
As it is difficult to evaluate strength of the very small particles of acicular titanium dioxide, Young's modulus of titanium dioxide is compared with other materials in the following table.
| Quartz | Potassium Titanate | Titanium Dioxide (Rutile) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Young's modulus (GPa) | 52~111 | 27.6 | 289.4 |
